Please find below Goldgenie’s Diamond Chart to compliment our SuperStar Range of solid gold and diamond iPhone’s.
Goldgenie Diamond Chart: The 4 C’s
Invented by De Beers in 1939, the standards largely adopted by the diamond industry are known as the 4Cs: Cut, Clarity, Color and Carat. To further refine this classification De Beers has introduced a new process of evaluation of the quality of diamonds, called “Brilliance.”
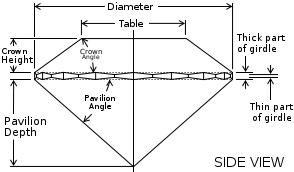
CUT
The term cut refers to the facets, and their proportions, on the surface of a diamond. At De Beers, we specifically prescribe the precise proportions of every diamond we offer. We operate within stringently applied guidelines and explicitly defined relationships between the table, the crown, the pavilion and the girdle of every stone.
De Beers diamonds are always cut for beauty, not weight. This steadfast belief is at the heart of our expertise. Carat weight is wrongly thought by many to be the most important factor in deciding the value of a diamond. Unfortunately, this misconception has led some diamond cutters to take advantage of the first-time buyer. For example, some diamond cutters will leave an excessively thick girdle around the stone, increasing the diamond’s carat weight. This practice harms the stone, considerably impairing the diamond’s beauty and brilliance. De Beers’ strict standards insist that we routinely sacrifice significantly more of the rough diamond than custom would normally dictate. Our exceptionally gifted craftsmen always prioritize the aesthetic above the raw weight of a rough diamond. They continuously go to immeasurable lengths to create precise, intricate angles that generate incomparable beauty.
THE MOST FREQUENT MISTAKES IN CUT
AN INCORRECT NUMBER OF FACETS: A round brilliant diamond from De Beers has 57 facets. Experience has shown that this is the most effective number to optimize the reflection of the light. Having a greater number of facets does not produce a diamond of higher quality. In fact, increasing the number of facets reduces the brilliance.
EXCESSIVE WEIGHT: Contrary to popular belief, excessive weight reduces aesthetic appeal. Since the number of carats is often considered as the most important criterion with regard to a diamond’s value, one common trick is to leave too thick a girdle. This gives the diamond more carats and therefore a higher price. Unfortunately, it also considerably diminishes the brilliance and beauty.
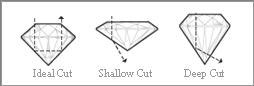
THE “LARGE ANGLE” EFFECT: When a diamond is given a flat cut and too large a table, the stone is dulled. Even worse, it produces an unattractive large angle effect across the crown.
THE “NAIL HEAD” EFFECT: If the cut of the diamond is too deep, a dark nail head may appear in the center of the stone.
DIAMOND SHAPE
Cut shouldn’t be confused with “shape.” Shape refers to the general outward appearance of the diamond, (such as round, emerald, or pear). When De Beers refers to cut, we are referring to the diamond’s reflective qualities, not the shape.
CLARITY
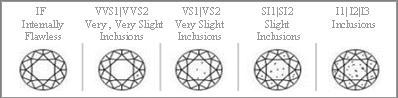
A diamond’s clarity rating is the key measure of its overall quality. Alas, nature guarantees that almost all diamonds have inherent natural blemishes called “inclusions.” Often, these clarity shortcomings are invisible to the untrained eye. However, these same imperfections are immediately apparent to our professional gemologists. The De Beers Institute of Diamonds operates with the highest standards in the industry, continuously and unequivocally rejecting diamonds that do not meet our criteria. A stone is said to be flawless if, under magnification, no inclusions like “clouds,” “pinpoints,” or internal crystals; no internal flaws, sometimes referred to as “feathers;” and no external imperfections, such as scratches, burns or abrasions, are visible.
THE MOST OBVIOUS FLAWS
CLOUDING: Milky clouding can produce a dull stone. The degree of penetration into the diamond affects the overall purity of the stone.
SUBSTANTIAL CRYSTALLIZATION: All natural diamonds, even the best, have a slight internal crystallization: a mark that occurs as the crystal forms. However, substantial crystallization constitutes a considerable flaw on the surface and sometimes in the depth of the diamond. It is manifested by veins, waves or minuscule cracks.
NODES: It is not unusual to see a diamond crystal, or node, within the diamond, which reaches up to the surface of the stone. While these imperfections are often accepted, De Beers does not use stones with nodes.
NATURALS: Some gem cutters leave a part of the original surface of the crystal in its rough state when cutting the facets of a diamond. These parts are called “naturals,” and they can change the appearance of the diamond. De Beers gemologists reject diamonds with naturals.
COLOUR
In nature, the absence of any color is very rare as most diamonds contain tiny amounts of nitrogen. The untrained eye may not be able to detect these minute variations of color, but these distinctions affect the rarity and ultimately the value of your diamond. De Beers subjects all the diamonds it uses to a customary color examination, regardless of any previous evaluations.
The color of every De Beers diamond is skillfully determined by the De Beers Institute of Diamonds. We compare every diamond to a De Beers Ideal Master diamond. Color is then rated according to a precise scale, running from “D” (colorless) to “Z” (saturated). If a stone has a borderline color classification, we assign it the lower rating. Past “Z” a diamond’s color is considered “fancy.” Fancy colored diamonds are very valuable and, correspondingly, are graded by very different parameters.
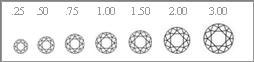
CARAT
A carat is equivalent to .2 grams and is the unit of weight for diamonds. The De Beers Institute of Diamonds can measure diamonds down to 1/1000 of a carat.
The value of a diamond increases in an exponential manner. Consequently, in the rare cases when two stones are of the same quality, the larger will have the greater value. A two-carat diamond for example will be worth more than two times a one-carat diamond of the same quality. Larger diamonds of high quality are extremely rare and are valued to reflect that rarity.


Comments